
The Nucleus of the Atom and Radioactivity
Atom: Definition, Structure & Parts with Labeled Diagram Atom Atoms are tiny particles that form the basic building blocks of all matter in the universe, whether solid, liquid, or gas. All living organisms and nonliving objects found on Earth are made of trillions and trillions of atoms.
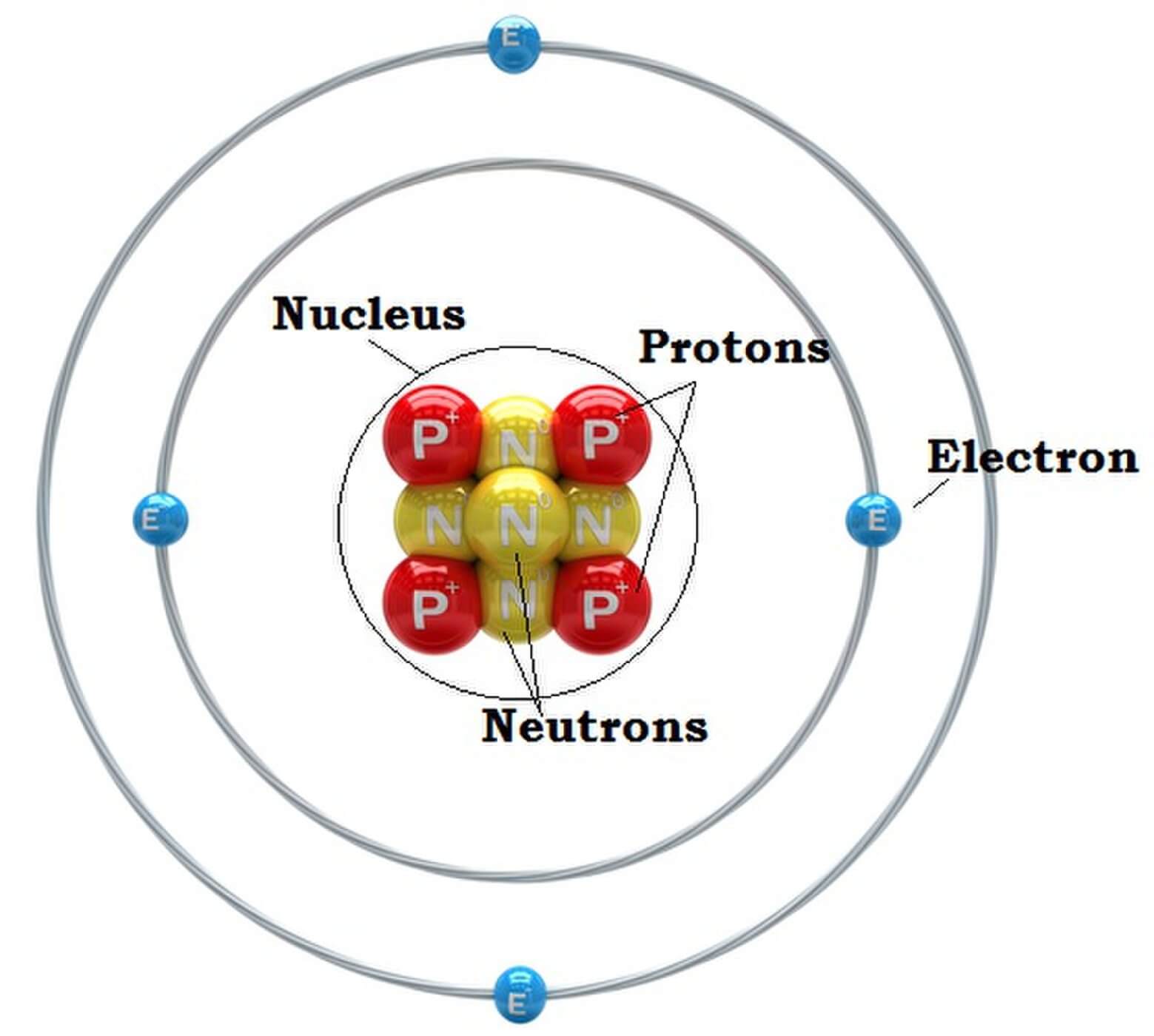
What is an Atom? Definitions & Examples Let us learn Basics News Bugz
Mass number. It is total number of proton and neutron present in the nucleus of each atom of an element. Mass number = No. of proton + no of neutrons. = atomic number - no of neutron. For example: the mass number of fluorine is 19 and atomic number is 9. Thus the number of neutron in an atom of fluorine is 19-9 =10.
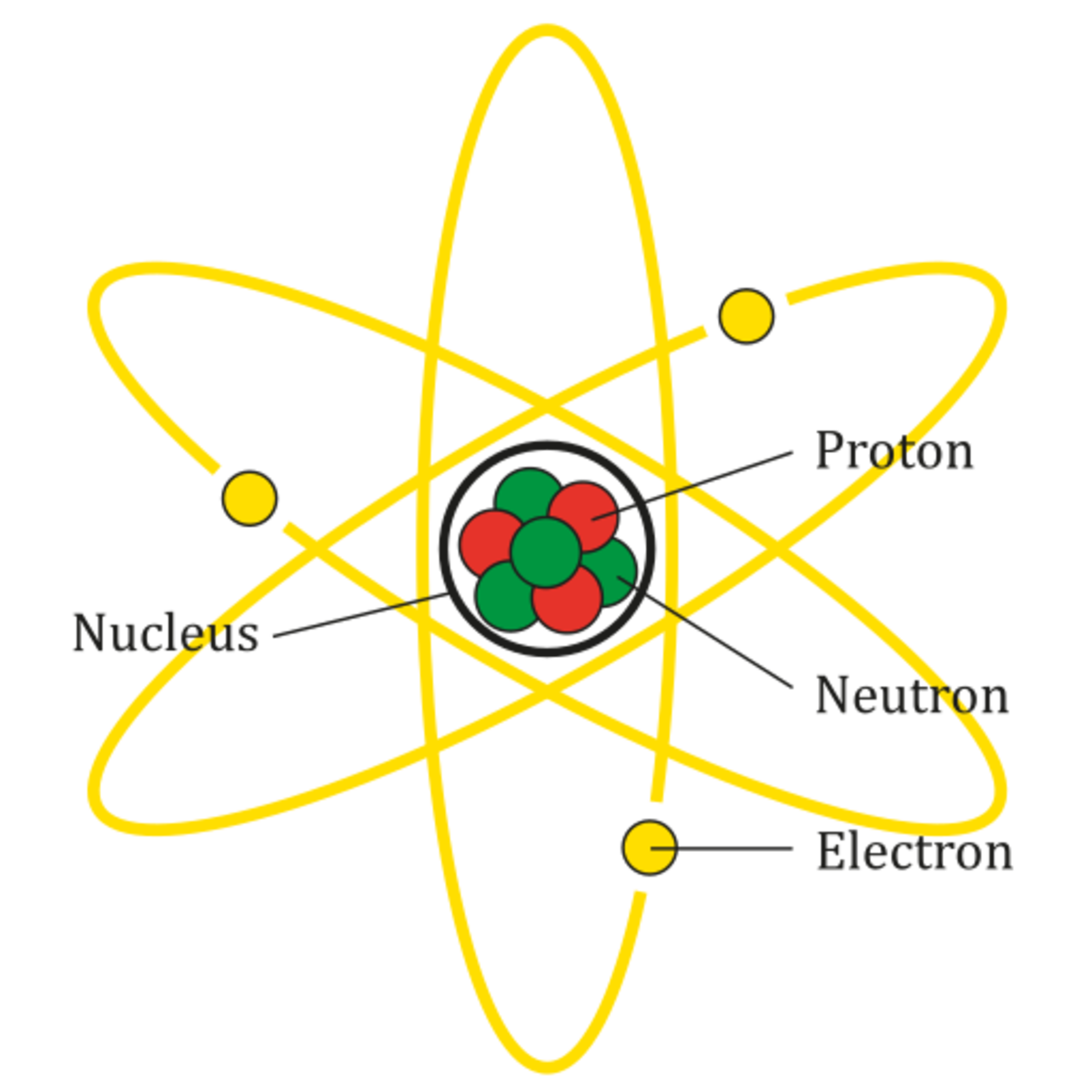
Atoms, Molecules, and Compounds What's the Difference? Owlcation
1. Draw five protons in the nucleus of the atom. Label them with their charge. 2. Draw six neutrons in the nucleus of the atom. 3. Draw two electrons in the first energy level and label them with their charge. 4. Draw three electrons in the second energy level and label them with their charge. 5. What element is represented by the diagram?
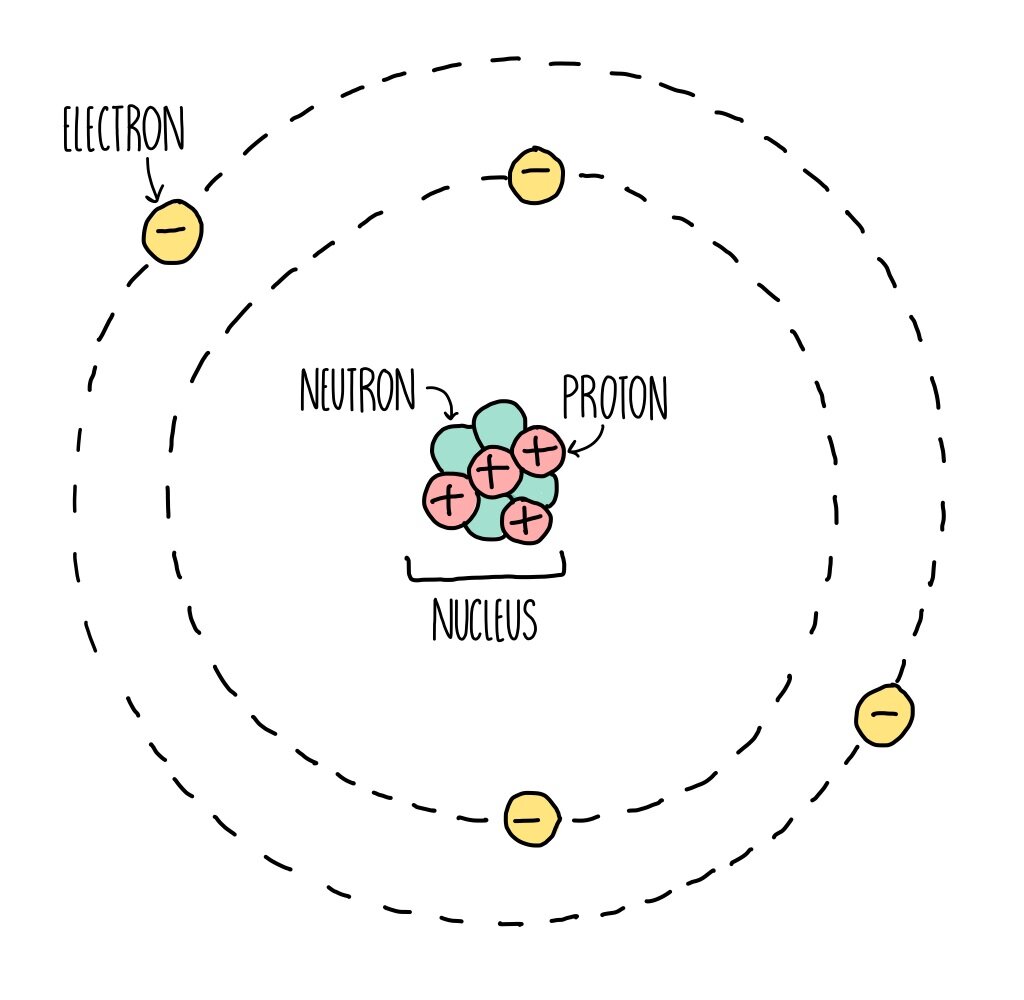
Atomic Structure (GCSE) — the science hive
Because the sum of the numbers of protons and neutrons equals the mass number, 127, the number of neutrons is 74 (127 − 53 = 74). Since the iodine is added as a 1− anion, the number of electrons is 54 [53 - (1-) = 54]. Exercise 2.2.1 2.2. 1. An ion of platinum has a mass number of 195 and contains 74 electrons.
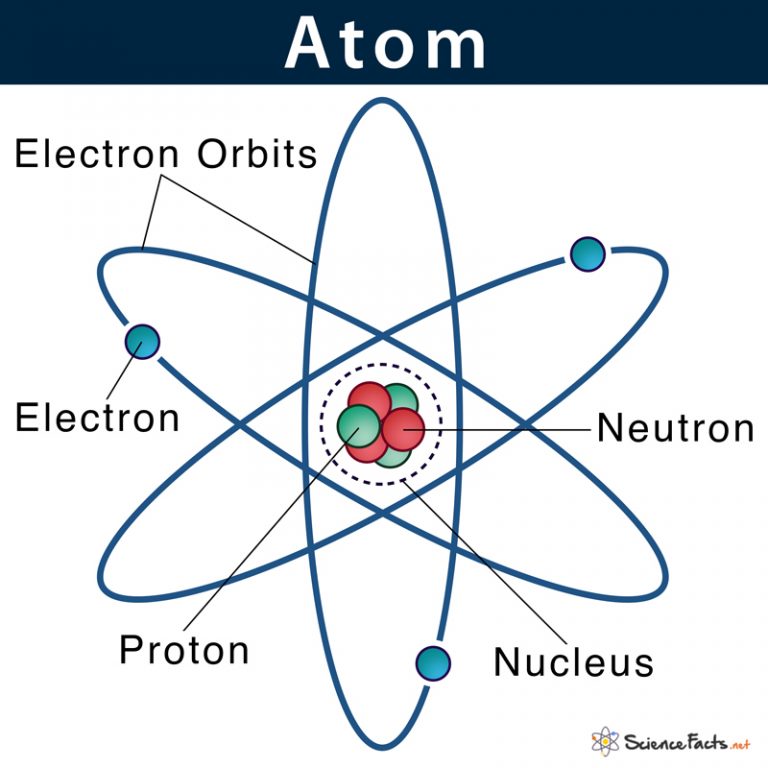
Atom Definition, Structure & Parts with Labeled Diagram
Our current model of the atom can be broken down into three constituents parts - protons, neutron, and electrons. Each of these parts has an associated charge, with protons carrying a positive.

Structure Of An Atom Class 9 Science Notes Leverage Edu
Atom The atom is the basic particle of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically-bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished from each other by the number of protons that are in their atoms.
/GettyImages-141483984-56a133b65f9b58b7d0bcfdb1.jpg)
35 Label The Parts Of The Atom In The Diagram Below Labels For Your Ideas
The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale The masses close mass The amount of matter an object contains. Mass is measured in kilograms (kg) or grams (g). of subatomic particles are very tiny.
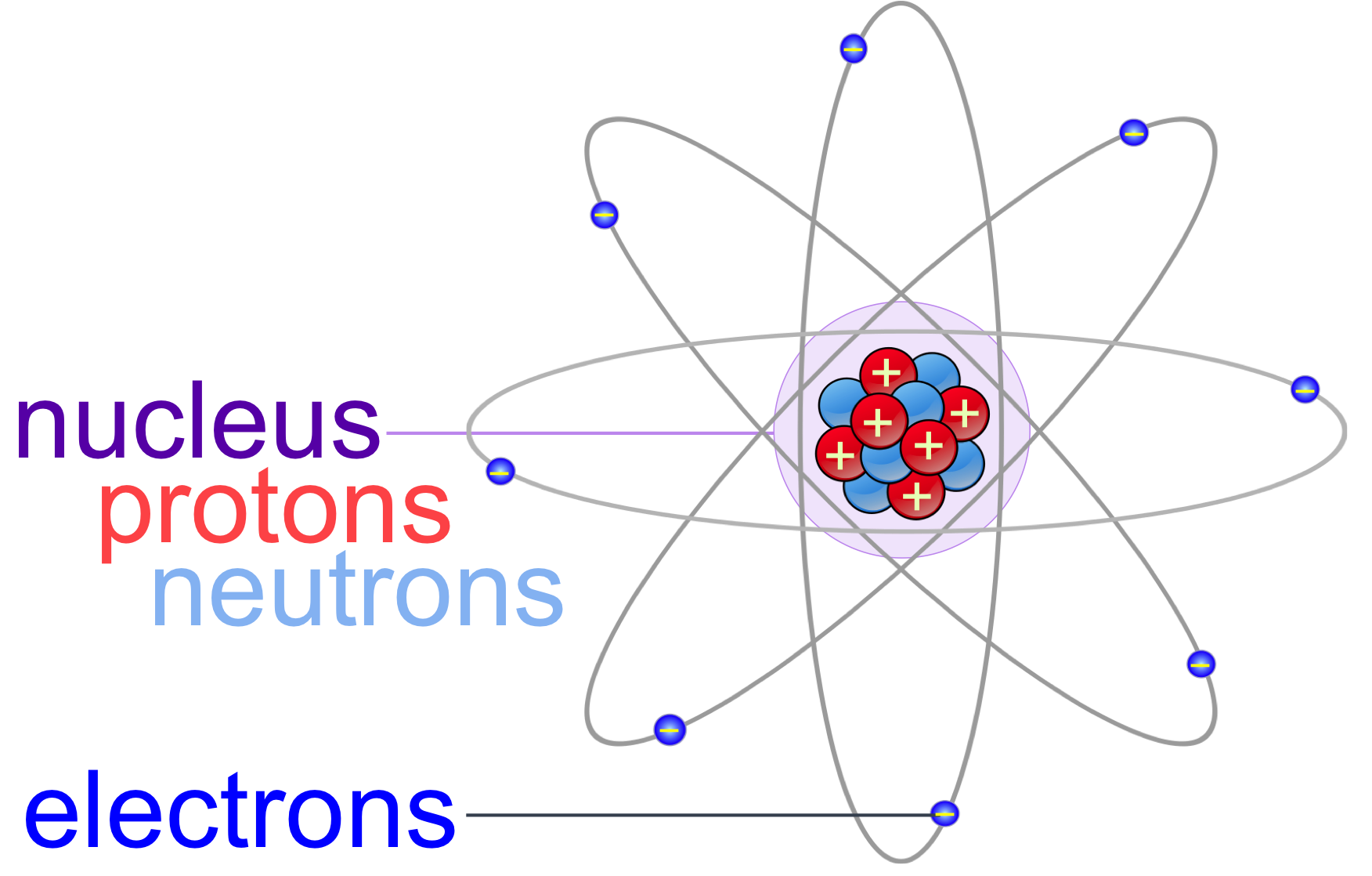
Atoms & Molecules echapter — The Biology Primer
An ion of an atom is one in which the number of protons and electrons is not the same. If there are more protons than electrons, an atomic ion has a positive charge and is called a cation. If there are more electrons than protons, the ion has a negative charge and is called an anion.
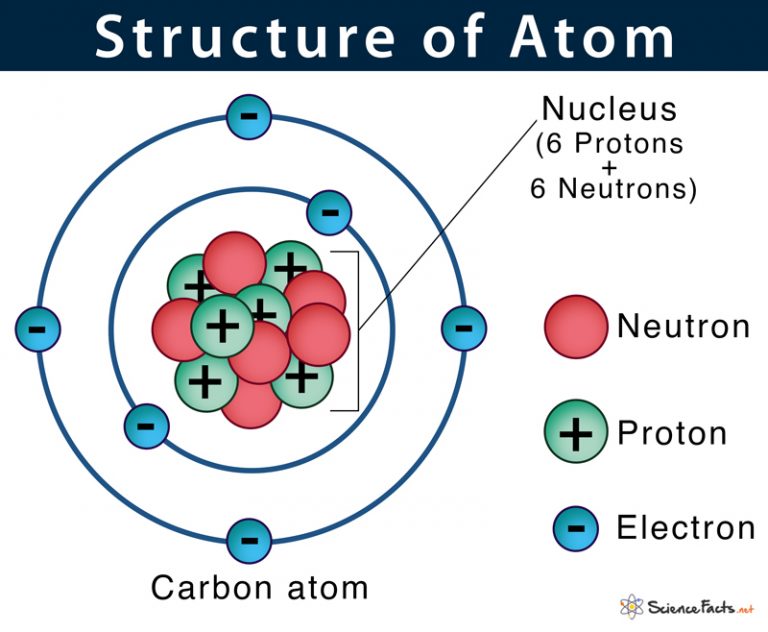
atom diagram to label
Key Points. An atom is composed of two regions: the nucleus, which is in the center of the atom and contains protons and neutrons, and the outer region of the atom, which holds its electrons in orbit around the nucleus. Protons and neutrons have approximately the same mass, about 1.67 × 10 −24 grams, which scientists define as one atomic.
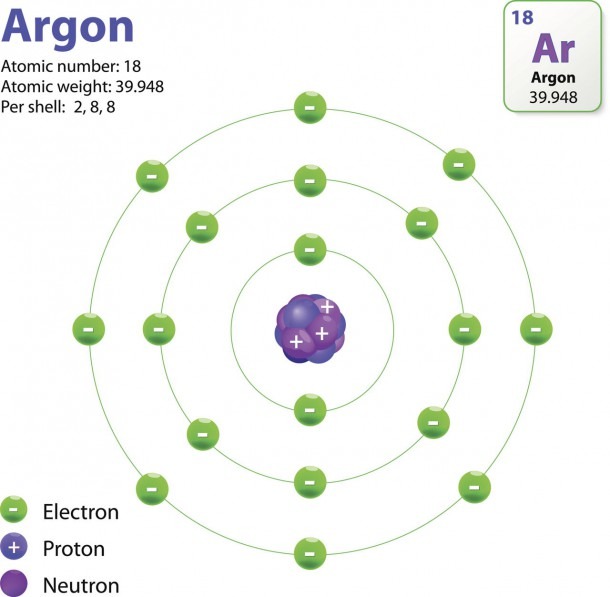
The Structure Of An Atom Explained With A Labeled Diagram Best Diagram Collection
Physical Chemistry (Essentials) - Class 11 8 units · 52 skills. Unit 1 Welcome to physical chemistry. Unit 2 Structure of atom. Unit 3 Some basic Concepts of Chemistry. Unit 4 Redox reactions. Unit 5 Gaseous state. Unit 6 Thermodynamics. Unit 7 Chemical Equilibrium. Unit 8 Ionic equilibrium.
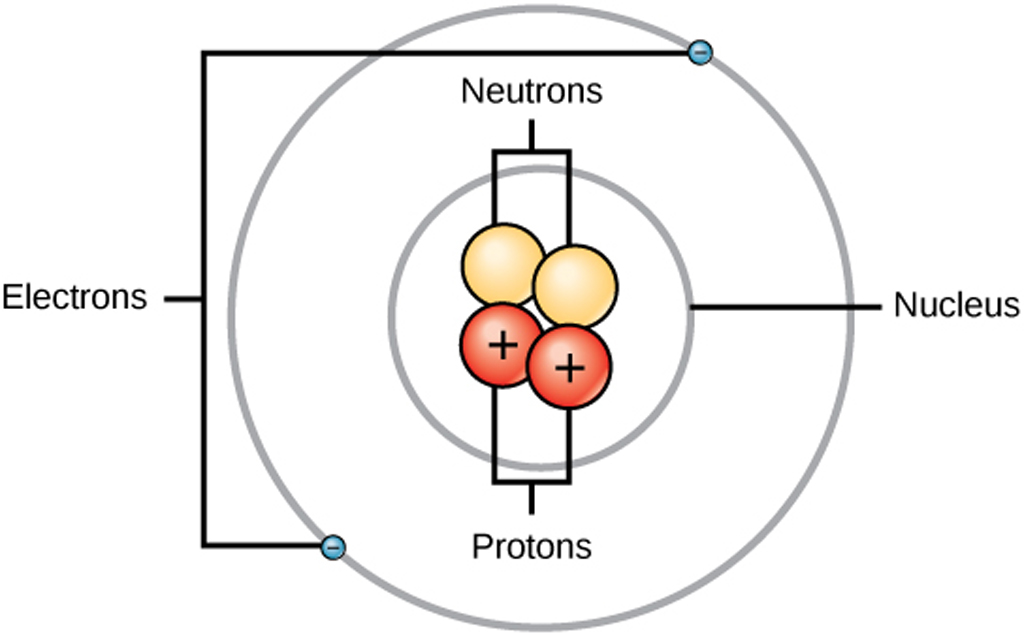
Structure of an Atom Structure & Use of Electron & Proton in Electronics
Figure 2.2.1 2.2. 1: The Structure of the Atom. Atoms have protons and neutrons in the center, making the nucleus, while the electrons orbit the nucleus. The modern atomic theory states that atoms of one element are the same, while atoms of different elements are different.
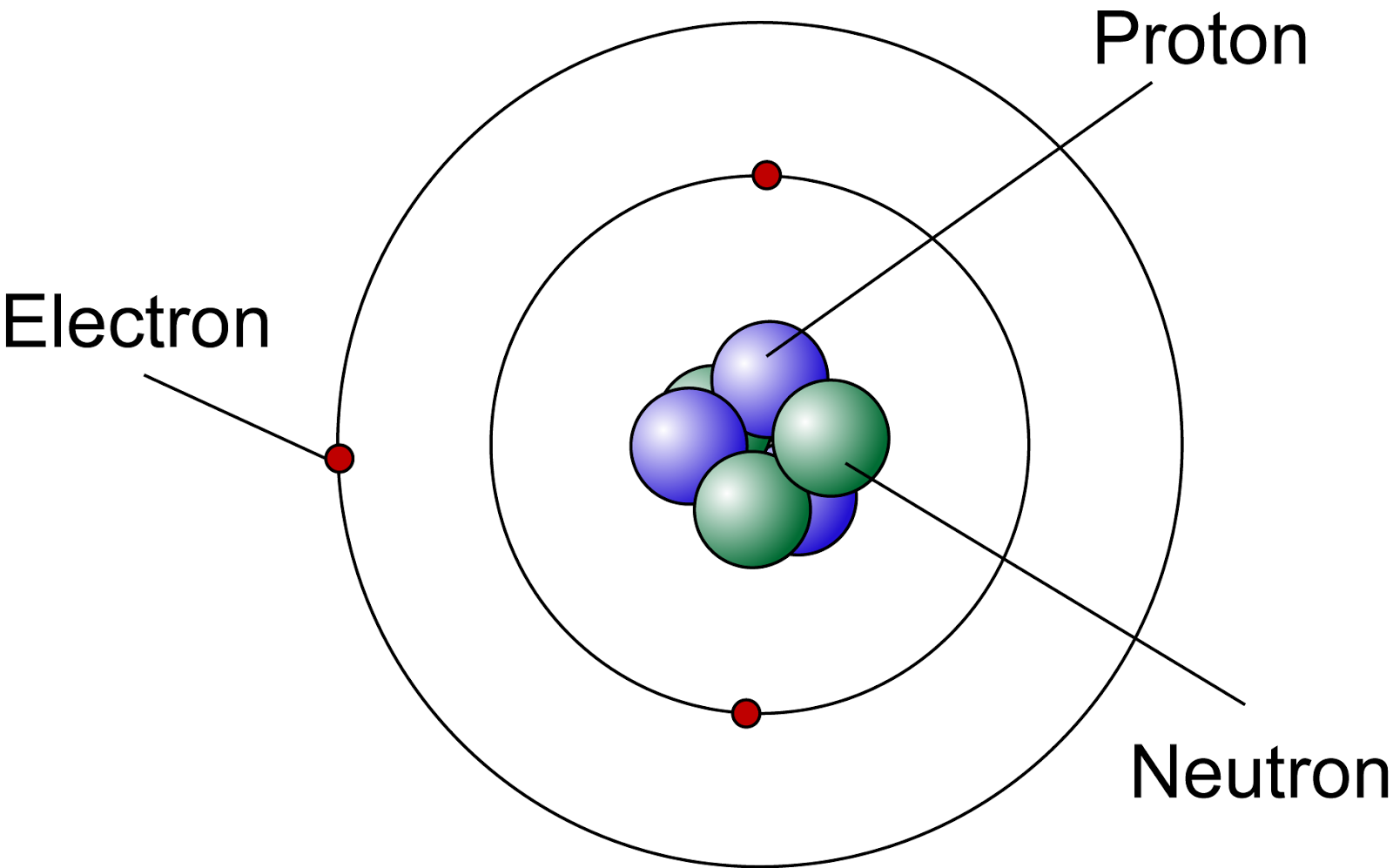
Lets Get Inside An Atom!! The Science Station
All atoms are roughly the same size, whether they have 3 or 90 electrons. Approximately 50 million atoms of solid matter lined up in a row would measure 1 cm (0.4 inch). A convenient unit of length for measuring atomic sizes is the angstrom (Å), defined as 10 −10 metre. The radius of an atom measures 1-2 Å.
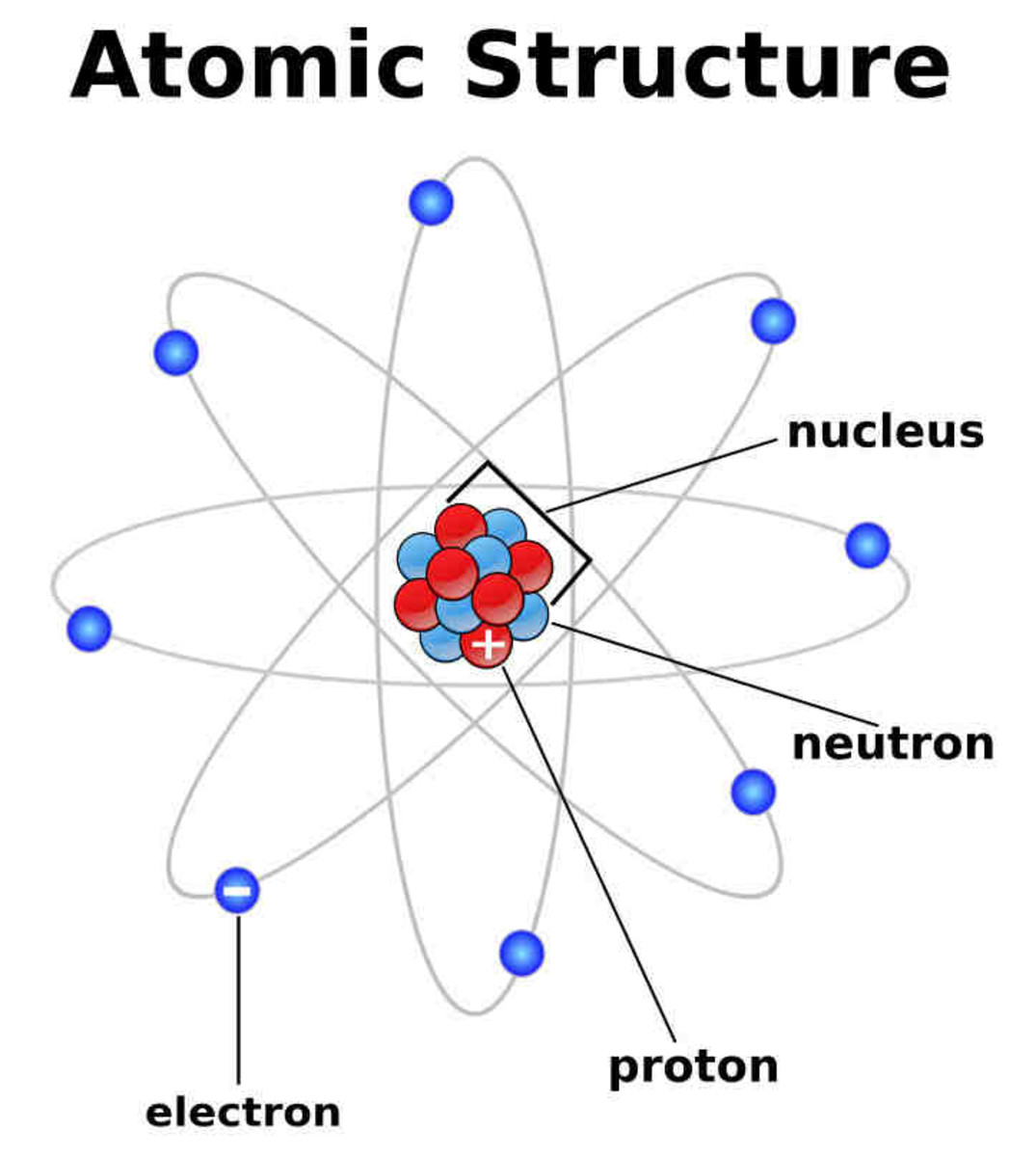
Atoms and Atomic Structure HubPages
In this video we cover the structure of atoms, what are subatomic particles, energy levels, and stable and reactive atoms.Transcript and notesAtomic structur.
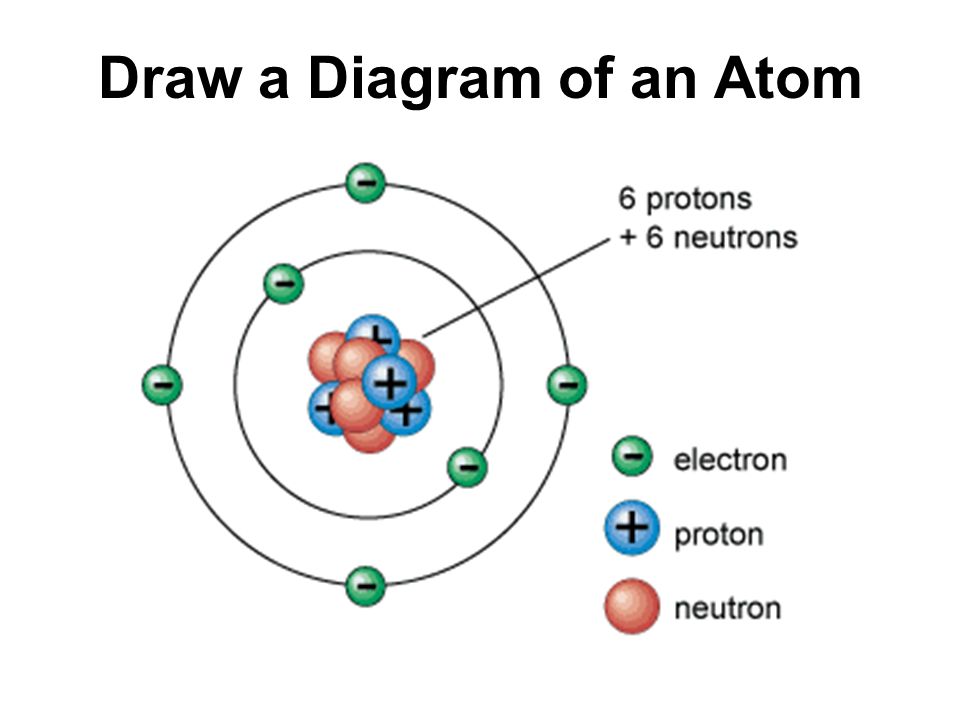
Skills Practice AMAZING 8TH GRADE SCIENTISTS
Figure three is a schematic diagram of a helium atom in its lowest energy state. Two protons are present in the nucleus of all helium atoms. In the most common variety of helium, the nucleus also contains two neutrons, which have nearly the same mass as the proton but carry no charge. Two electrons orbit the nucleus.
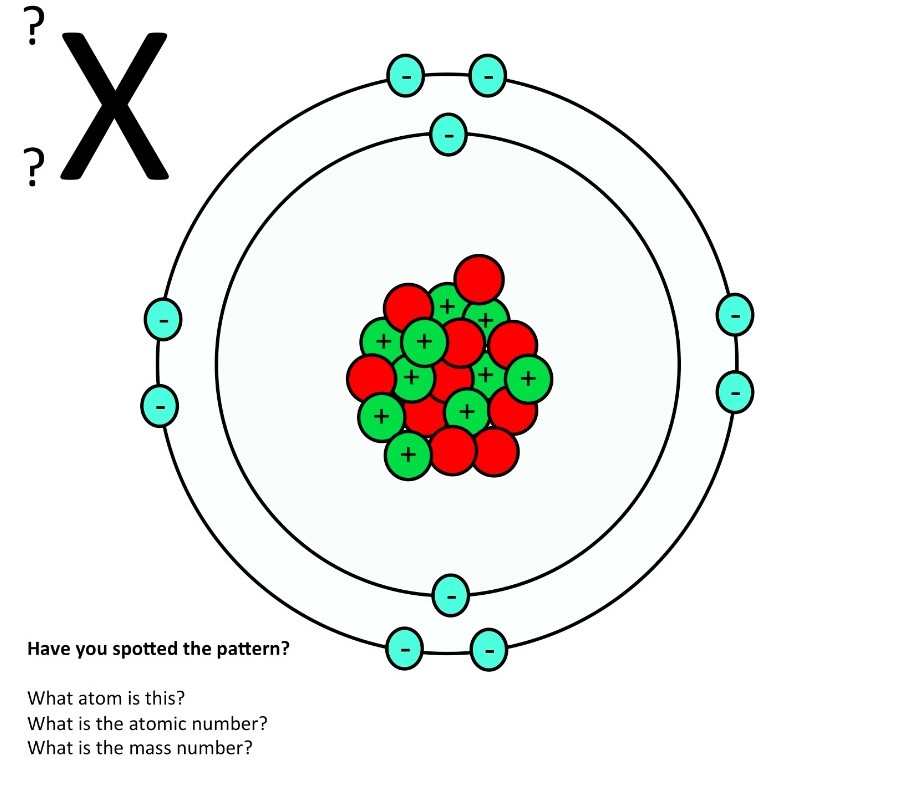
Atomic structure teaching resources the science teacher
proton. Definition. Positively charged particle found in the nucleus of an atom. Location. Term. nucleus. Definition. The center of the atom which contains protons and neutrons. Location.

Atomic Structure Broad Learnings
Parts of the Atom Part 1 - Label the parts of the atom below (protons, neutrons, electrons, nucleus, quarks). + + +----+ to the nucleus)? Part 2 - Answer the following questions. 1. _____What part of the atom has no charge? 2. _____What part of the atom has a positive charge? 3. _____What part of the atom has a negative charge? 4.